Redis 跳跃表相关源码阅读笔记,源码文件 server.h & t_zset.c。
1. 小结
在 Redis 中实现的跳跃表:
- 最大层数为 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
- 跳跃表中不允许相同的
ele,允许相同的 score,按 <score, ele> pair 进行排序
- 增加
backward 指针,可反向遍历跳跃表
2. 跳跃表相关数据结构
跳跃表之于普通链表,如同增加快速通道的地铁线路之于单一地铁线路,从普通到特急停靠站越来越少,因此到达目的地所需时间也越短。跳跃表也是利用“快速通道”使得查找、插入和删除等操作更高效,可通过阅读维基百科了解详情。
Redis 中跳跃表大致基于论文Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees实现,但有三处改动:
- 允许相同的
score
- 比较不仅仅是基于
score 的大小
- 增加
backward 指针,用于反向遍历
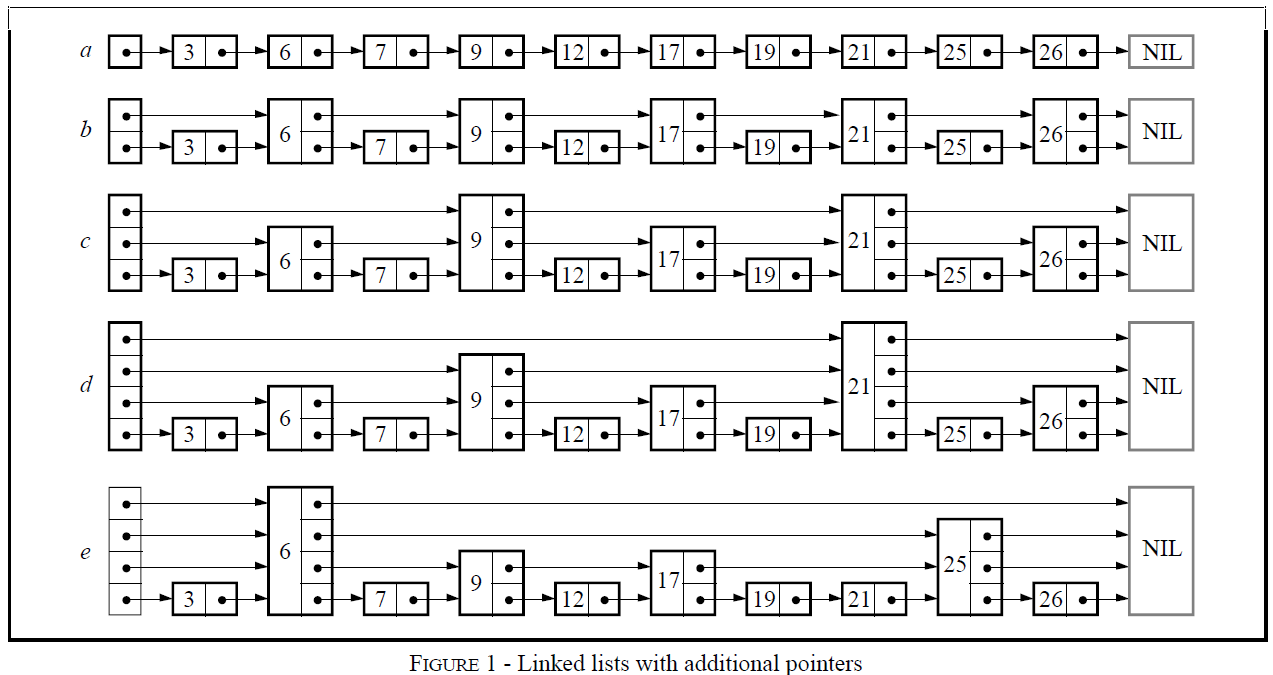
跳跃表 zskiplist 的结构如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
|
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
unsigned long length;
int level;
} zskiplist;
|
header 和 tail 分别指向跳跃表的头尾节点length 记录该跳跃表中节点个数level 记录该跳跃表中除头节点外其他节点的最大层数,其上限为 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
在跳跃表中,每个节点 zskiplistNode 的结构如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
|
ele: member 的地址,不允许相同的 memberbackward: 指向前一节点level[]: 每个节点含有复数层的遍历通道,每一层包含在该层下一节点的地址 forward,以及此时的步长 span,当 forward 为 NULL 时,span 等于 0
此外,还有表示 score 区间的 zrangespec 和 ele 区间的 zlexrangespec,定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/* Struct to hold a inclusive/exclusive range spec by score comparison. */
typedef struct {
double min, max;
int minex, maxex; /* are min or max exclusive? */
} zrangespec;
/* Struct to hold an inclusive/exclusive range spec by lexicographic comparison. */
typedef struct {
sds min, max; /* May be set to shared.(minstring|maxstring) */
int minex, maxex; /* are min or max exclusive? */
} zlexrangespec;
|
3. 跳跃表 APIs
3.1. 构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels.
* The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */
zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele);
/* Create a new skiplist. */
zskiplist *zslCreate(void);
|
初始化时,zsl->level 等于 1,头节点的 level 数组长度为 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
3.2. 析构函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/* Free the specified skiplist node. The referenced SDS string representation
* of the element is freed too, unless node->ele is set to NULL before calling
* this function. */
void zslFreeNode(zskiplistNode *node);
/* Free a whole skiplist. */
void zslFree(zskiplist *zsl);
|
3.3. 插入节点
zslRandomLevel
1
2
3
4
5
|
/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create.
* The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
* (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher
* levels are less likely to be returned. */
int zslRandomLevel(void);
|
返回一个随机的 level,设 ZSKIPLIST_P 为 $p$,ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 为 $ml$ 则 level 值 $i$ 与其对应的概率 $P(i)$ 满足下式:
$$
P(i) =
\begin{cases}
(1-p)p^{i-1}, & i \ne ml \cr
1 - \Sigma_{i=1}^{ml - 1}P(i), & i = ml \cr
\end{cases}
$$
zslInsert
1
2
3
4
|
/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already
* exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership
* of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele);
|
插入一个新节点至跳跃表,调用方应保证 ele 此前不存在于跳跃表 zsl 中。插入操作流程如下:
-
按照 level 从大到小寻找每一层中最靠近($<$)新节点的目标节点并记录其地址 (该目标节点 score 小于新节点 socre 或 score 相同时 ele 小于新节点 ele)
-
调用 zslRandomLevel 给新节点生成一个随机的 level 值,若该 level 值大于 zsl->level,则将为 zsl->level 至 level 每层最靠近新节点的目标节点初始化为头节点,随后更新 zsl->level 值
-
根据 level、score 和 ele 值调用 zslCreateNode 创建新节点,并将其插入跳跃表中,更新新节点以及每层中最靠近新节点的目标节点的 level 数组的内容:
- 新节点
level 值大于之前 zsl->level 时,每层目标节点的 forward 和 span 都需更新
- 新节点
level 值小于之前 zsl->level 时,0 -> level 层目标节点的 forward 和 span 都需更新,而 level -> zsl->level 层目标节点只需更新 span 值
-
更新新节点和其后一节点(level = 0)的 backward 指针
-
更新 zsl->length
可以看出,在跳跃表中查找操作和在不考虑换乘时间的情况下最快到达目的车站所采取的策略相同,要点有二:
- 尽可能搭乘快速列车,也即要在该层找到新节点的左极限
- 不要坐过站,也即每次在该层新节点的左极限时跳转至下层,寻找更接近新节点的跳跃表节点,直至最底层
3.4. Score range APIs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
/* Populate the rangespec according to the objects min and max.
*
* Parse the min-max interval. If one of the values is prefixed
* by the "(" character, it's considered "open". For instance
* ZRANGEBYSCORE zset (1.5 (2.5 will match min < x < max
* ZRANGEBYSCORE zset 1.5 2.5 will instead match min <= x <= max */
static int zslParseRange(robj *min, robj *max, zrangespec *spec);
/* Returns if there is a part of the zset is in range. */
int zslIsInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range);
/* Find the first node that is contained in the specified range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
zskiplistNode *zslFirstInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range);
/* Find the last node that is contained in the specified range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
zskiplistNode *zslLastInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range);
|
3.5. Lexicographic range APIs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
/* Parse max or min argument of ZRANGEBYLEX.
* (foo means foo (open interval)
* [foo means foo (closed interval)
* - means the min string possible
* + means the max string possible
*
* If the string is valid the *dest pointer is set to the redis object
* that will be used for the comparison, and ex will be set to 0 or 1
* respectively if the item is exclusive or inclusive. C_OK will be
* returned.
*
* If the string is not a valid range C_ERR is returned, and the value
* of *dest and *ex is undefined. */
int zslParseLexRangeItem(robj *item, sds *dest, int *ex);
/* Free a lex range structure, must be called only after zelParseLexRange()
* populated the structure with success (C_OK returned). */
void zslFreeLexRange(zlexrangespec *spec);
/* Populate the lex rangespec according to the objects min and max.
*
* Return C_OK on success. On error C_ERR is returned.
* When OK is returned the structure must be freed with zslFreeLexRange(),
* otherwise no release is needed. */
int zslParseLexRange(robj *min, robj *max, zlexrangespec *spec);
/* Returns if there is a part of the zset is in the lex range. */
int zslIsInLexRange(zskiplist *zsl, zlexrangespec *range);
/* Find the first node that is contained in the specified lex range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
zskiplistNode *zslFirstInLexRange(zskiplist *zsl, zlexrangespec *range);
/* Find the last node that is contained in the specified range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
zskiplistNode *zslLastInLexRange(zskiplist *zsl, zlexrangespec *range);
|
由于跳跃表是按照 score 排序的,因此 zslFirstInLexRange 返回的节点可能比 zslLastInLexRange 返回的节点位置靠后。
3.6. 删除节点
zslDeleteNode
1
2
3
|
/* Internal function used by zslDelete, zslDeleteRangeByScore and
* zslDeleteRangeByRank. */
void zslDeleteNode(zskiplist *zsl, zskiplistNode *x, zskiplistNode **update);
|
从跳跃表 zsl 中删除指定的节点 x,传入的 update 数组记录了每层中最靠近(<) x 的节点地址。值得注意的是,在该函数中无释放操作。
zslDelete
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
/* Delete an element with matching score/element from the skiplist.
* The function returns 1 if the node was found and deleted, otherwise
* 0 is returned.
*
* If 'node' is NULL the deleted node is freed by zslFreeNode(), otherwise
* it is not freed (but just unlinked) and *node is set to the node pointer,
* so that it is possible for the caller to reuse the node (including the
* referenced SDS string at node->ele). */
int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele, zskiplistNode **node);
|
从跳跃表 zsl 中根据 score 和 ele 参数删除特定的节点。
- 该特定节点存在时,删除成功,返回 1,不存在时,删除失败,返回 0
- 传入的
node 不为 NULL 时,保存被删除节点的地址,node 为空时直接释放被删除节点所占内存
- 该函数会先寻找距离被删除节点最靠近的目标节点数组,然后调用
zslDeleteNode 执行删除操作
zslDeleteRangeBy…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/* Delete all the elements with score between min and max from the skiplist.
* Min and max are inclusive, so a score >= min || score <= max is deleted.
* Note that this function takes the reference to the hash table view of the
* sorted set, in order to remove the elements from the hash table too. */
unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByScore(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range, dict *dict);
/* Delete all the elements with ele between min and max from the skiplist. */
unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByLex(zskiplist *zsl, zlexrangespec *range, dict *dict);
/* Delete all the elements with rank between start and end from the skiplist.
* Start and end are inclusive. Note that start and end need to be 1-based */
unsigned long zslDeleteRangeByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned int start,
unsigned int end, dict *dict);
|
3.7. zslUpdateScore
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
/* Update the score of an elmenent inside the sorted set skiplist.
* Note that the element must exist and must match 'score'.
* This function does not update the score in the hash table side, the
* caller should take care of it.
*
* Note that this function attempts to just update the node, in case after
* the score update, the node would be exactly at the same position.
* Otherwise the skiplist is modified by removing and re-adding a new
* element, which is more costly.
*
* The function returns the updated element skiplist node pointer. */
zskiplistNode *zslUpdateScore(zskiplist *zsl, double curscore, sds ele, double newscore);
|
- 调用方需确保根据
cursorce 和 ele 匹配的节点必须存在在跳跃表中
- 如果
newscore 不改变节点次序,该函数会就地更新指定节点的 score 值,否则会先从跳跃表中删除原节点,再根据 ele 和 newsocre 重新插入新节点
3.8. Get APIs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
/* Find the rank for an element by both score and key.
* Returns 0 when the element cannot be found, rank otherwise.
* Note that the rank is 1-based due to the span of zsl->header to the
* first element. */
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele);
/* Finds an element by its rank. The rank argument needs to be 1-based. */
zskiplistNode* zslGetElementByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned long rank);
|

